CBSE CLASS 12 POLITICAL SCIENCE NCERT SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 5 SECURITY IN CONTEMPORARY WORLD - HUMANITAS
NCERT Solutions & Questions CBSE Class 12 Chapter 5 SECURITY IN CONTEMPORARY WORLD
This article provides comprehensive NCERT Solutions for CBSE CLASS 12 POLITICAL SCIENCE CHAPTER 5 SECURITY IN CONTEMPORARY WORLD. Completing all NCERT questions is essential for all school and board examinations.
We also offer Different Solutions which students from Class 11 & 12 face during their CBSE boards exam preparations and also during their CUET UG preparations. Please check them out:
1. Match the terms with their meaning:
i. Confidence Building Measures (CBMs)
ii. Arms Control
iii. Alliance
iv. Disarmament
a. Giving up certain types of weapons
b. A process of exchanging information on defence matters between nations on a regular basis
c. A coalition of nations meant to deter or defend against military attacks
d. Regulates the acquisition or development of weapons
Answer:
i. Confidence Building Measures (CBMs) - (b) A process of exchanging information on defence matters between nations on a regular basis.
ii. Arms Control - (d) Regulates the acquisition or development of weapons.
iii. Alliance - (c) A coalition of nations meant to deter or defend against military attacks.
iv. Disarmament - (a) Giving up certain types of weapons.
2. Which among the following would you consider as a traditional security concern, non-traditional security concern, or not a threat?
a. The spread of chikungunya/dengue fever
b. Inflow of workers from a neighbouring nation
c. Emergence of a group demanding nationhood for their region
d. Emergence of a group demanding autonomy for their region
e. A newspaper that is critical of the armed forces in the country
Answer:
a. The spread of chikungunya/dengue fever - Non-traditional security concern.
b. Inflow of workers from a neighbouring nation - Non-traditional security concern.
c. Emergence of a group demanding nationhood for their region - Traditional security concern.
d. Emergence of a group demanding autonomy for their region - Not a threat.
e. A newspaper that is critical of the armed forces in the country - Not a threat.
See: Study like a topper - Join Humanitas Online Class 12 Batch
3. What is the difference between traditional and non-traditional security? Which category would the creation and sustenance of alliances belong to?
Answer:
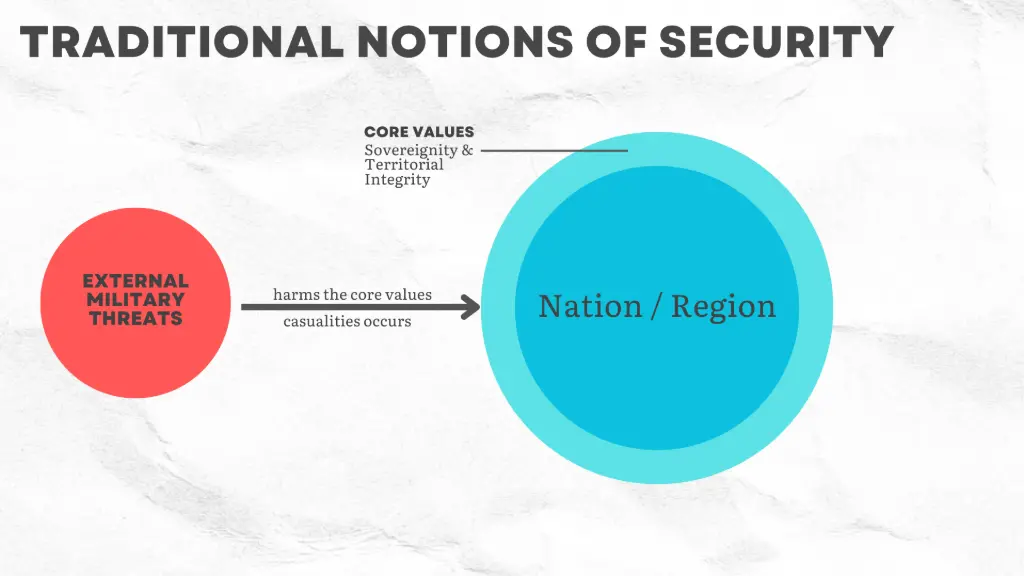
Traditional security focuses on protecting a nation from military threats through the measures like deterrence and defense, promoting state sovereignty and territorial integrity.
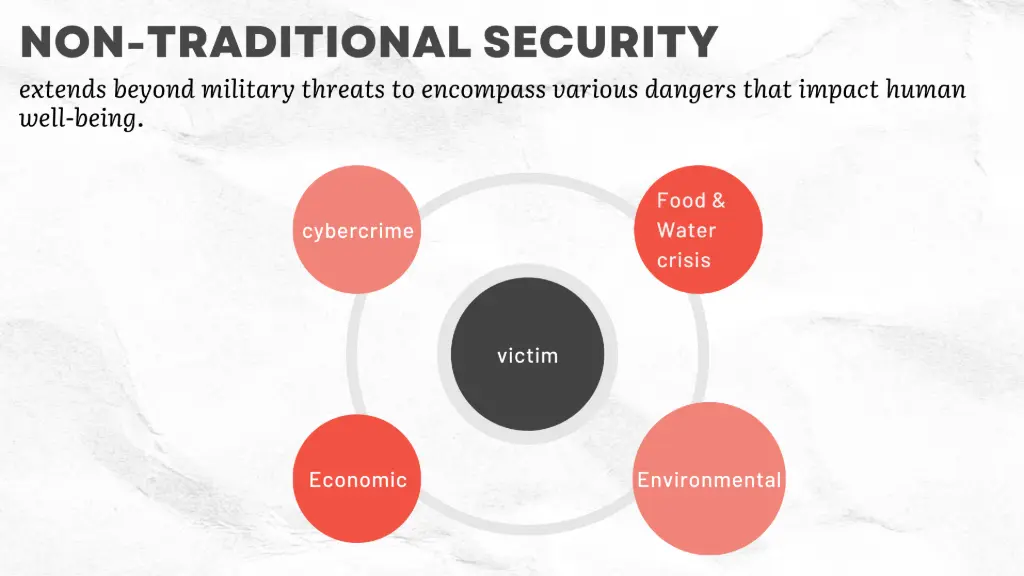
Non-traditional security includes a broader range of challenges, which covers health epidemics, migration, and environmental issues, while focus on human and global security beyond mere military aspects.
The creation and maintaning of alliances fall under traditional security, as they involve coalitions formed to deter or defend against military attacks.
4. What are the differences in the threats that people in the Third World face and those living in the First World face?
Answer:
Following are the differences in the threats that people in the Third World face and those living in the First World face:
Third World countries, face many threats such as military conflicts with neighboring states and internal challenges from separatist movements which seek independence.
These nations suffer with both external aggression and internal aggression. In comparison, First World countries experience stable internal conditions and are more focused on external threats.
5. Is terrorism a traditional or non-traditional threat to security?
Answer:
Terrorism is considered a non-traditional threat to security. It involves political violence by targeting civilians indiscriminately, while aiming to create fear and achieve their political objectives.
Unlike traditional military threats from other nations, terrorism often originates from non-state actors and employs unconventional methods, such as hijackings and bombings in public places which results into casualties.
6. What are the choices available to a state when its security is threatened, according to the traditional security perspective?
Answer:
When faced with security threats, a state has three primary options:
- Surrender to the opponent, though this is rarely adopted as official policy.
- Deterrence: Preventing an attack by raising the costs of war or a,unitions to an unacceptable level for the aggressor to match.
- Defense: Actively protecting oneself when war occurs, to deny the attacker their objectives and to defeat their forces.

7. What is ‘Balance of Power’? How could a state achieve this?
Answer:
The 'Balance of Power' is a concept in international relations where power is distributed among various nations to prevent any one state from dominating others.
A state can achieve BoP by building up its military capabilities, forming alliances with other nations, and engaging in diplomacy to counterbalance threats, which ensures that no single entity becomes powerful.
8. What are the objectives of military alliances? Give an example of a functioning military alliance with its specific objectives.
Answer:
- Military alliances are formed with the objective of deterring or defending against military attacks through collective security arrangements.
- Member nations agree to mutual defense and often coordinate their military strategies and resources.
- For e.g., North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which aims to safeguard the freedom and security of its members through political and military means.
See: Study like a topper - Join Humanitas Online Class 12 Batch
9. Rapid environmental degradation is causing a serious threat to security. Do you agree with the statement? Substantiate your arguments.
Answer:
Yes, rapid environmental degradation poses a serious threat to security.
- Environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution can lead to resource scarcity, which in turn may cause conflicts over water, food, and energy.
- It can result in natural disasters and loss of livelihoods, leading to mass migrations and social unrest, thereby destabilizing regions and increasing security challenges.
10. Nuclear weapons as deterrence or defence have limited usage against contemporary security threats to states. Explain the statement.
Answer:
- Nuclear weapons are primarily designed as deterrents against large-scale military aggression from other states.
- But, nowadays, security threats increasingly stem from non-traditional sources such as terrorism, cyber-attacks, and environmental crises, against which nuclear weapons are ineffective.
- These challenges require alternative approaches, including intelligence sharing, international cooperation, and sustainable development, rather than reliance on nuclear arsenals.
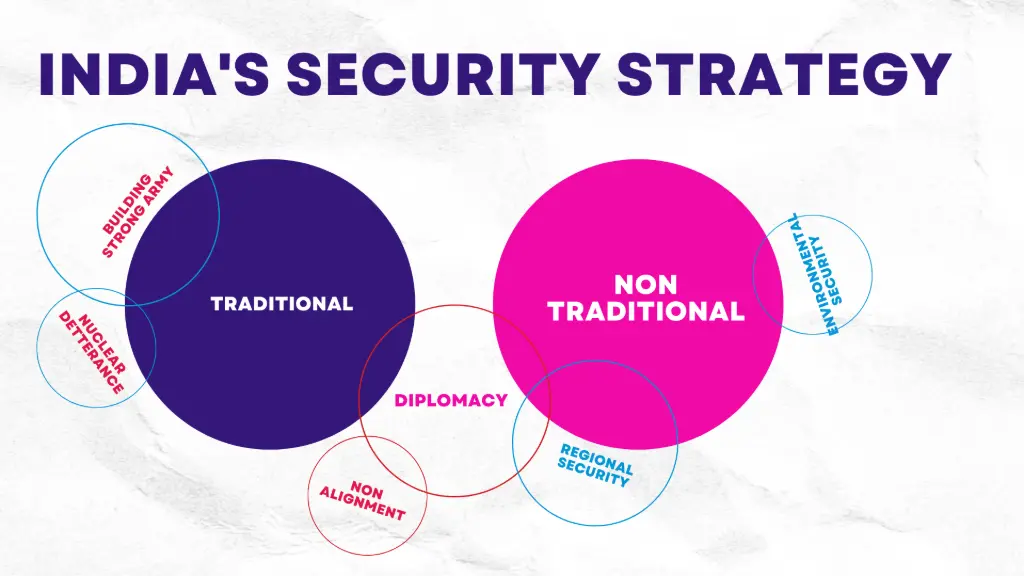
11. Looking at the Indian scenario, what type of security has been given priority in India—traditional or non-traditional? What examples could you cite to substantiate the argument?
Answer:
- India has historically prioritized traditional security concerns, focusing on military preparedness and defense against external threats, evidenced by its significant defense budget and strategic actions.
- But, in recent years, there has been a growing recognition of non-traditional security issues.
- For example,, initiatives like the National Action Plan on Climate Change and various public health programs indicate an increasing emphasis on environmental challenges and health crises.
12. Read the cartoon below and write a short note in favour or against the connection between war and terrorism depicted in this cartoon.
Answer:
The cartoon illustrates the cyclical relationship between war and terrorism, which suggests that military actions can sometimes lead to increased terrorism, and vice versa. It emphasizes the need for useful strategies that address the root causes of terrorism, rather than relying solely on military interventions.
Note: Do well in CLASS 12 humanities, through our Humanitas Expert New Session Batch.
With daily classes, weekly tests, live Google Meet doubt clearing with experienced subject experts, chapter-wise MCQ Mock tests based on CBSE Patterns & trends, detailed notes, and so much more, you'll get the guidance you need until exam day.
Explore Other resources from Humanitas:
- Syllabus for CBSE Board exams 2025
- Important Questions for CBSE Board Exams 2025
- Date sheet CBSE Board Exams 2025
- NCERT Books for CBSE Board Exams 2025
- Sample Question papers for CBSE Board Exams 2025
- Admit Card for CBSE Board Exams 2025
- Preparation strategy for CBSE Board Exams 2025
- CBSE Board Exams 2025 Overview
CBSE CLASS 12 POLITICAL SCIENCE NCERT SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 5 SECURITY IN CONTEMPORARY WORLD - HUMANITAS